What is RAM? Exploring the Basics of Random Access Memory
RAM, the cornerstone of computer memory, powers our digital experiences. It fuels applications, empowers multitasking, and ensures smooth execution.
RAM is the swift messenger shuttling data to and from CPUs. It shapes the computing landscape, enhancing speed and responsiveness.
Without RAM, computing would be sluggish, hindering productivity and creativity. But what exactly is RAM and how does it shape computing?
Let’s delve into this remarkable component armed with compelling statistics.
Windows holds 76.15% of the global desktop market share, relying on RAM. The global computer memory market is projected to reach $200 billion by 2027.
RAM is indispensable, fueling our hunger for computing power and technological advancements.
Join us as we unravel the mysteries of RAM and its pivotal role.
Get ready for a captivating journey into the world of RAM.
What is RAM? Definition of RAM Explained!
How RAM Works?
- Power On: When you turn on your computer, power is supplied to the RAM modules.
- Initialization: The computer’s hardware and firmware initialize the RAM, preparing it for operation.
- Addressing: Each byte of data in RAM is assigned a unique address, allowing for precise storage and retrieval.
- Data Storage: Information, including program instructions and data, is stored in RAM as a temporary workspace.
- Read and Write: The processor sends requests to read or write data to specific memory addresses.
- Data Transfer: Upon a read request, the RAM quickly sends the requested data to the processor.
- Updating Data: When a write request is received, the RAM updates the specified memory location with new data.
- Access Speed: RAM’s high-speed circuits enable rapid data access. It is much faster than traditional storage devices.
- Volatility: RAM is volatile memory, meaning its contents are lost when power is turned off.
- Data Availability: As long as the computer is powered on, data stored in RAM is readily available for processing.
- Temporary Storage: RAM acts as a temporary storage medium, holding data while the computer is active.
- Efficient Processing: RAM enables speedy execution of instructions by facilitating fast access and retrieval.
Comparison of RAM with other types of memory (e.g., hard disk)
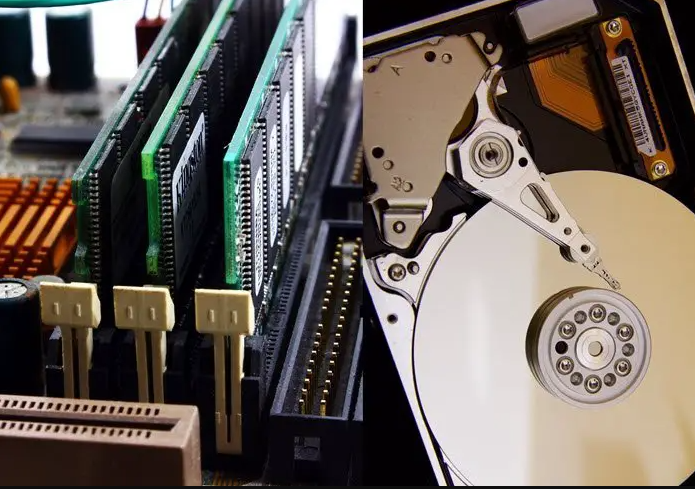
Random access and Read/write operations in RAM!
RAM allows the processor to retrieve and change data randomly, unlike sequential access memory. By providing random access, RAM enables data retrieval regardless of its location.
RAM offers read and write capabilities, facilitating data retrieval and storage. This bi-directional functionality enhances system speed and responsiveness.
Understanding RAM and its distinctions is crucial for optimizing system performance. By utilizing RAM effectively, users can harness its rapid data access capabilities.
Efficient RAM usage enhances multitasking, program execution, and system efficiency.
RAM Capacity and Types!
A. Factors affecting RAM capacity
- Different OS versions and features influence recommended RAM capacity.
- Resource-intensive applications may require higher RAM capacities.
- Larger RAM helps switch between programs smoothly during multitasking.
- Anticipate future software advancements and opt for slightly larger capacity.
B. Overview of different RAM types
-
-
- DDR4 (Double Data Rate 4): Common in modern systems, it offers higher data transfer rates, capacities, and power efficiency than DDR3.
- DDR5 (Double Data Rate 5): Next-generation RAM with even higher data transfer rates and capacities than DDR4, introducing new features for improved performance and efficiency.
- Other RAM Types: Previous generations like DDR3, DDR2, and DDR exist but offer lower performance and capacities compared to DDR4 and DDR5.
-
C. Considerations for selecting the appropriate RAM capacity
- System Requirements: Check recommended RAM capacity for optimal performance.
- Budget Constraints: Find balance between performance and budget when choosing capacity.
- Future Upgradability: Leave room for expansion if system allows RAM upgrades.
- Personal Usage Patterns: Opt for larger capacity for resource-intensive tasks like gaming or video editing.
By understanding the factors influencing RAM capacity and considering system requirements, budget, future upgradability, and personal usage patterns, users can select the optimal RAM configuration for their needs, maximizing system performance and meeting computing requirements.
Impact of RAM on Performance
A. Relationship between RAM and multitasking capabilities
- RAM plays a crucial role in multitasking by allowing the system to handle multiple programs simultaneously.
- Sufficient RAM capacity ensures that each program has the necessary space to store its data and instructions, reducing the need for constant swapping of data between RAM and storage devices.
- With ample RAM, the system can keep more programs and data readily accessible, enabling smoother and more efficient multitasking without significant performance degradation.
B. Influence of RAM on system speed and responsiveness
- RAM directly impacts the speed and responsiveness of a computer system.
- When programs are loaded into RAM, they can be accessed and executed by the processor at significantly faster speeds compared to accessing data from storage devices.
- With more RAM available, the system can keep a larger portion of frequently accessed data in RAM, reducing the time spent on data retrieval and improving overall system responsiveness.
- Insufficient RAM can lead to frequent data swapping between RAM and storage devices, causing delays, system slowdowns, and decreased responsiveness.
C. Effects of insufficient RAM on overall performance and potential solutions
- Insufficient RAM can result in performance bottlenecks, especially when running resource-intensive applications or multitasking with numerous programs.
- When RAM reaches its capacity limit, the system compensates by utilizing slower storage devices, leading to increased load times, program lag, and decreased overall performance.
- To address insufficient RAM, users can consider upgrading their RAM modules to increase the capacity. This allows for smoother multitasking, faster program execution, and improved system performance.
- Another solution is to optimize RAM usage by closing unnecessary programs, reducing the number of background processes, and managing system resources efficiently.
Understanding RAM’s impact on performance is crucial. It is because to optimize system resources and ensuring a smooth computing experience. Adequate RAM capacity enables efficient multitasking and enhances system speed and responsiveness. Insufficient RAM can cause performance issues. It is important to recognize the correlation between RAM and multitasking abilities. Also understand how RAM affects system speed, and explore possible solutions.
Factors Influencing RAM Requirements
A. Types of Applications and Workloads
- Resource-Intensive Applications: Applications like video editing software, 3D modeling tools, or virtual machines require larger amounts of RAM to handle the extensive data processing and manipulation involved.
- Gaming Laptops: Modern games often have higher RAM requirements, especially for seamless gameplay and faster loading times. The complexity of the game, graphics quality, and the size of in-game environments contribute to RAM needs.
- Office/Productivity Tasks: General office tasks, web browsing, document editing, and email management typically require less RAM compared to resource-intensive applications or gaming.
B. Operating System Requirements
- Each operating system has minimum RAM requirements for smooth operation. These requirements vary depending on the specific version and edition of the operating system.
- Additional RAM may be needed to accommodate the operating system’s background processes, services, and utilities that run concurrently with user applications.
C. Multitasking and Usage Patterns
- Multitasking: Users who frequently switch between multiple applications or run multiple programs simultaneously will benefit from a larger RAM capacity. This ensures smooth transitions and prevents performance degradation due to data swapping.
- Usage Patterns: The nature of tasks and applications used by an individual impacts their RAM requirements. For example, professional video editors or graphic designers working with large files may require more RAM compared to casual users.
D. Future-Proofing and Upgradability
- Considering future software advancements and increasing resource demands, it is advisable to anticipate higher RAM needs when selecting RAM capacity.
- Leaving room for future upgrades allows for easy expansion of RAM when required, ensuring compatibility with upcoming software updates or more demanding applications.
E. Budget Constraints
- Budget considerations play a role in determining the RAM capacity one can afford.
- Users should strike a balance between their performance requirements and budget limitations to select the most suitable RAM configuration.
Understanding RAM requirements involves considering different factors. Like application types, operating system demands, multitasking, usage patterns, future-proofing, and budget constraints. This knowledge helps users select the right RAM capacity. Ensuring optimal performance and a smooth computing experience.
Factors Affecting RAM Performance
A. RAM Speed
- RAM speed refers to the rate at which data can be transferred to and from the RAM module.
- Higher RAM speeds result in faster data transfer and improved overall system performance.
- The speed of RAM is measured in megahertz (MHz), and it is important to ensure compatibility with the motherboard’s supported RAM speed.
B. RAM Timings
- RAM timings, also known as latency, determine the time it takes for the RAM to respond to the processor’s requests.
- Lower RAM timings indicate faster response times and better performance.
- RAM timings are represented by a series of numbers, such as 16-18-18-36, where each number represents a specific latency value.
C. Dual-Channel and Quad-Channel Memory
- Dual-channel and quad-channel memory configurations involve using multiple RAM modules to improve memory bandwidth and performance.
- Dual-channel memory uses two identical RAM modules, while quad-channel memory utilizes four identical modules, providing higher data transfer rates.
- To take advantage of dual-channel or quad-channel memory, the motherboard and CPU must support these configurations.
D. RAM Compatibility with Motherboard
- It is crucial to ensure that the selected RAM modules are compatible with the motherboard.
- Check the motherboard’s specifications, including the supported RAM type, speed, and maximum capacity.
- Additionally, consider the motherboard’s available RAM slots and their configuration for optimal performance.
E. Overclocking RAM
- Overclocking RAM involves running the memory modules at higher frequencies than their default specifications.
- Overclocking can provide a performance boost, but it requires proper cooling and careful adjustment of voltage and timings.
- It is important to note that overclocking RAM may void warranties and can potentially cause system instability if not done correctly.
Understanding RAM performance factors helps optimize memory configuration. Consider RAM speed, timings, and memory configurations. Check compatibility with the motherboard. Explore the potential of overclocking. Make informed decisions for maximum RAM performance. Select appropriate modules and configure them correctly. Enhance system speed and responsiveness. Improve overall computing experience.
How to Check RAM Capacity on Windows 10?
Checking the RAM capacity on a Windows 10 computer is a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Open Start Menu: Click “Start” button at bottom left of the screen.
- Access System Settings: Click gear-shaped “Settings” icon in Start Menu.
- Navigate to System Settings: In Windows Settings window, click “System” option.
- View RAM Capacity: In System settings, click “About” tab on left side. On the right side, find “Installed RAM” or “Installed memory (RAM)” section to view total RAM capacity in GB.
Alternatively, you can also use the following method to check RAM capacity:
- Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc: This keyboard shortcut will open the Task Manager directly.
- Access Performance Tab: In the Task Manager window, navigate to the “Performance” tab by clicking on it.
- View RAM Capacity: In the Performance tab, you will find various performance-related information, including the RAM capacity. Look for the “Memory” or “Memory (RAM)” section to view the total installed RAM capacity in gigabytes (GB).
By following these steps, you can easily check the RAM capacity on a Windows 10 computer. Knowing the installed RAM capacity helps in understanding the available resources and making informed decisions regarding system upgrades or optimizing software usage.
How to Check RAM Capacity on Mac Computers?
Checking the RAM capacity on a Mac computer is a simple process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Click on the Apple Menu: Located at the top-left corner of the screen, click on the Apple logo to open the Apple Menu.
- Access “About This Mac”: In the Apple Menu, select the “About This Mac” option. A new window will appear with detailed information about your Mac.
- View Installed RAM: In the “About This Mac” window, click on the “Memory” tab. Here, you will find information about your Mac’s RAM, including the total installed capacity. The RAM capacity will be displayed in gigabytes (GB).
Alternatively, you can use the following method to check RAM capacity:
- Open “Applications” and Locate “Utilities”: Click on the “Finder” icon in the dock, then navigate to the “Applications” folder. Within the “Applications” folder, open the “Utilities” folder.
- Launch “Activity Monitor”: In the “Utilities” folder, find and open the “Activity Monitor” application. This utility provides various information about system resources.
- Access the “System Memory” Tab: In the “Activity Monitor” window, click on the “System Memory” tab. This tab displays information about the Mac’s memory usage and capacity.
- View RAM Capacity: In the “System Memory” tab, you will find the total installed RAM capacity listed as “Memory” or “Physical Memory” in gigabytes (GB).
By following these steps, you can easily check the RAM capacity on a Mac computer. Understanding the installed RAM capacity helps in assessing available resources and making informed decisions about system upgrades or optimizing software usage.
Determining Adequate RAM Capacity
Determining the appropriate RAM capacity for your specific needs requires considering various factors. Here are some key considerations to help you determine the right amount of RAM:
- Application Requirements: Check RAM specifications for your regular applications, especially resource-intensive ones.
- Multitasking Needs: More RAM aids efficient multitasking with multiple applications or large datasets.
- Operating System Recommendations: Ensure RAM meets or exceeds minimum requirements for your OS.
- Future-Proofing: Anticipate future needs and aim for RAM capacity that accommodates potential upgrades.
- Budget Considerations: Balance RAM capacity with budget constraints while meeting requirements.
- User Experience and Performance Expectations: More RAM enhances multitasking, program load times, and responsiveness.
- Consult Manufacturer Recommendations: Follow guidelines provided by your computer manufacturer.
- Upgrade Possibilities: Assess motherboard support for higher RAM capacities and available RAM slots.
Consider these factors to determine the right RAM capacity for your needs. It enhances system performance and ensures a smooth computing experience. Strike a balance between requirements, budget, and future-proofing to make an informed decision.
Is 2 GB of RAM Enough?
Having 2 GB of RAM can be considered quite limited in today’s computing landscape. While it may be sufficient for basic tasks on older or less resource-intensive systems, it is generally inadequate for modern computing needs. Here are some points to consider:
- Basic Tasks: 2 GB RAM is suitable for web browsing, email, and document editing, but multitasking or demanding activities may cause performance issues.
- Operating System Requirements: Modern OSs like Windows 10 or macOS have higher RAM needs, allocating a significant portion to system processes.
- Performance Limitations: Limited RAM leads to data swapping with the hard drive, resulting in slower performance, longer program load times, and sluggishness.
- Multitasking Constraints: With 2 GB RAM, multitasking, switching apps, or having multiple browser tabs can cause delays and slowdowns.
- Resource-Intensive Applications: Video editing, gaming, or virtual machines require more RAM, which may be insufficient with only 2 GB.
2 GB of RAM has limitations that can be overcome by upgrading to a higher capacity. Increasing the RAM capacity provides a smoother and more efficient computing experience. Benefits include better multitasking, improved system responsiveness, and the ability to run demanding applications without performance issues.
Is 4 GB of RAM Enough?
4 GB of RAM is considered limited for demanding tasks and modern applications. Basic computing needs can be handled, but resource-intensive tasks may not be seamless. Consider the following key points:
- 4 GB RAM is suitable for web browsing, email, document editing, and multimedia playback without major issues.
- Modern OSs like Windows 10 or macOS demand more RAM, leaving less for user applications.
- 4 GB RAM allows light multitasking, but running multiple apps or browser tabs may degrade performance.
- Video editing, gaming, or virtual machines need more RAM for optimal performance.
- Upgrading RAM helps ensure compatibility with future software updates and increasing requirements.
- Consider budget limitations when determining the amount of RAM to upgrade.
Consider upgrading to a higher RAM capacity from 4 GB for improved performance. Recommended for resource-intensive tasks, multitasking, and modern applications. Increased RAM enhances system performance, responsiveness, and workload efficiency. Addresses limitations of 4 GB RAM.
Is 8 GB of RAM Enough?
Having 8 GB of RAM is generally considered sufficient for most users and can provide a smooth computing experience for a wide range of tasks. Here are some key points to consider:
- Multitasking and Productivity: 8 GB RAM allows seamless multitasking and smooth application switching, enhancing productivity.
- OS and Software Requirements: 8 GB RAM meets minimum requirements for modern OSs like Windows 10 or macOS, minimizing data swapping.
- Resource-Intensive Apps: 8 GB RAM handles photo/video editing, design, and moderate gaming well for most users.
- Future-Proofing: 8 GB RAM ensures compatibility with future software updates and offers a smoother experience.
- Budget Considerations: 8 GB RAM strikes a balance between performance and affordability.
- User Type: 8 GB RAM suffices for casual users and students, while power users or multimedia professionals may need more.
Overall, 8 GB of RAM is considered a sweet spot for most users, offering a good balance between performance, multitasking capabilities, and cost-effectiveness. It provides a smooth computing experience for a wide range of tasks and is suitable for casual users, students, and many professionals.
Is 16 GB of RAM Enough?
Having 16 GB of RAM is considered more than sufficient for the majority of users, including power users and professionals. It offers ample memory capacity to handle demanding tasks and resource-intensive applications. Here are some key points to consider:
- Multitasking and Performance: With 16 GB RAM, smooth multitasking and seamless task switching.
- Resource-Intensive Apps: 16 GB RAM handles video editing, 3D rendering, and virtual machines efficiently.
- Future-Proofing and Compatibility: 16 GB RAM ensures compatibility with future software and resource requirements.
- Gaming Performance: 16 GB RAM supports modern games with faster loading times and better graphics.
- Data Analysis and Virtualization: 16 GB RAM benefits data analysis, simulations, and virtualization tasks.
- Enhanced System Performance: 16 GB RAM improves overall system performance and responsiveness.
16 GB of RAM offers high performance and versatility for power users, professionals, and gamers. It provides headroom for demanding applications and large datasets. Ensures a future-proof computing experience. Not necessary for casual users or standard productivity tasks.
Is 32 GB of RAM Worth It?
Having 32 GB of RAM is generally considered overkill for most users, as it exceeds the requirements of typical computing tasks. However, there are specific scenarios where 32 GB of RAM can be beneficial. Here are some key points to consider:
- Professional Workstations: 32 GB RAM benefits video editing, 3D rendering, and complex simulations.
- Virtualization and Servers: 32 GB RAM ensures smooth operation of multiple virtual machines.
- Content Creation and Streaming: 32 GB RAM enhances productivity for tasks like live streaming and graphic design.
- Future-Proofing and Extended Lifespan: 32 GB RAM prepares your system for future resource demands.
- Niche Computing Needs: 32 GB RAM supports scientific research, data analysis, and large-scale databases.
- Gaming Enthusiasts: 32 GB RAM improves performance for advanced gaming setups and VR gaming.
It’s important to note that for typical day-to-day tasks, 32 GB of RAM may be excessive and not fully utilized. However, for professionals and users with specific demanding needs, the additional RAM can significantly enhance performance, productivity, and the ability to handle resource-intensive tasks.
Is 64 GB of RAM Overkill?
Having 64 GB of RAM is generally considered overkill for the vast majority of users, including most professionals and gamers. It exceeds the requirements of typical computing tasks. And is primarily beneficial for niche scenarios that demand extensive memory capacity. Here are some key points to consider:
- Specialized Workloads: 64 GB RAM suits memory-intensive tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, and scientific simulations.
- High-End Servers and Workstations: 64 GB RAM is ideal for running multiple virtual machines and managing extensive databases.
- Content Creation and Professional Design: 64 GB RAM benefits fields like animation and architectural design.
- Future-Proofing and Extended Lifespan: 64 GB RAM prepares for future software demands.
- Extreme Gaming Setups: 64 GB RAM enhances gaming performance for high-end setups and resource-intensive games.
It’s crucial to assess your specific needs and usage patterns before considering 64 GB of RAM. For most users, including professionals in many fields, 32 GB of RAM is generally more than sufficient. For niche applications or specialized workloads, 64 GB of RAM offers a performance boost. It accommodates the resource requirements of these tasks. Enhances memory capacity for demanding applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right RAM Capacity
Selecting the right RAM capacity depends on usage patterns, needs, and budget.
Key takeaways for choosing RAM:
- Assess your usage: Evaluate tasks, multitasking, and future needs.
- Consider operating system requirements: Meet or exceed recommended RAM specifications.
- Account for resource-intensive applications: Higher RAM for smoother performance.
- Future-proofing: Invest in slightly higher capacity for compatibility with updates.
- Budget constraints: Balance performance and cost.
- Seek balance and flexibility: Optimize RAM for current and future needs.
- Conclusion: 4 GB for basic tasks, 8 GB for most users, 16 GB for resource-intensive tasks, and 32 GB or 64 GB for specialized workloads.
Align your RAM choice with requirements for an optimal computing experience.