What is a Computer Mouse and Parts of a Mouse and its Functions!
A computer mouse is an important device that helps us interact with computers. It allows us to control a small arrow, called a cursor, on the screen. With the mouse, we can do things like
- point to items,
- select text,
- draw picture,
- scroll up & down,
- give commands using a graphical user interface (GUI).
It’s a handheld tool that makes using a computer easier and more convenient.
By moving the mouse and clicking its buttons, we can move around on the computer screen, open files, and do many other things.
The mouse was invented a long time ago, back in the 1960s, by a person named Douglas Engelbart. It was originally called the X-Y Position Indicator for a Display System.
Since then, the mouse has become very popular and is now found in almost every computer. Over the years, the mouse has been improved and developed to make it more useful and efficient.
To understand how a mouse works, it’s important to know about its different parts.
A mouse usually has buttons, a wheel, a cable (if it’s a wired mouse), ball or sensors to track movement, and a circuit board.
Each part has a specific job and helps us control the mouse and interact with the computer.
The mouse has many functions and uses.
We can use it to point to things on the screen, select text, draw pictures, move things around, scroll up and down on documents, and click to open files or give commands. It can also do other cool things like hovering over objects to get more information and playing games on the computer.
There are different types of computer mouse to choose from.
Some have a ball underneath to track movement, while others use optical sensors. There are also cordless mouse that connect without a wire and touchpads that are built into laptops.
Each type of mouse has its own advantages and is designed for specific needs.
In the next sections, we will learn more about the different parts of a mouse, how they work, the different types of mouse, and how to use and take care of them.
By understanding all these things, we can become more efficient and skilled computer users.
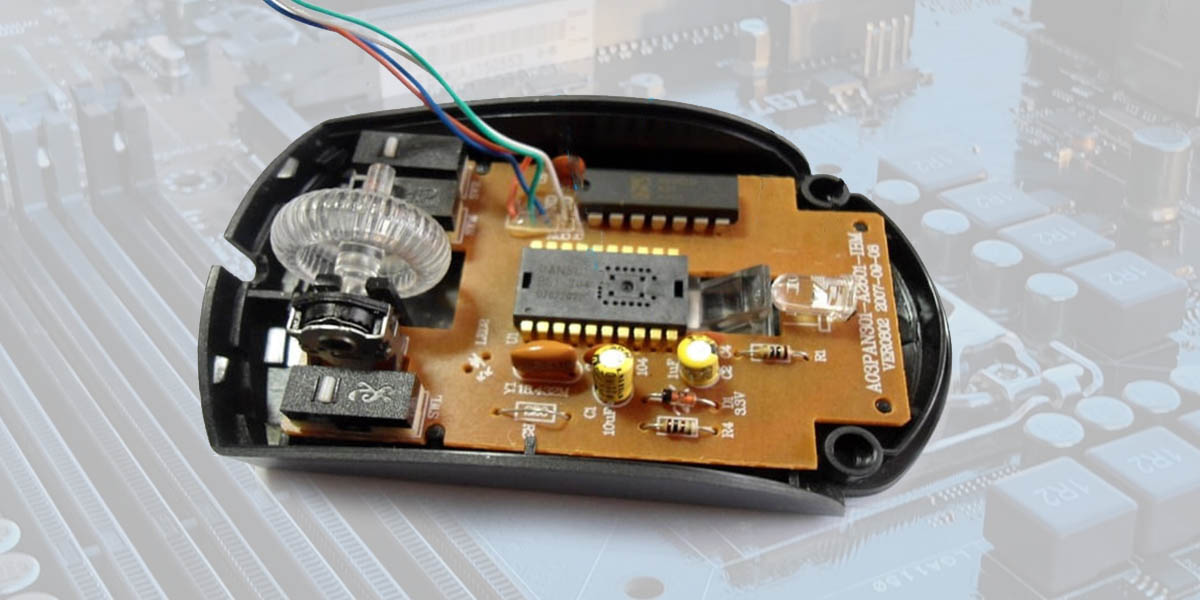
Parts of a Computer Mouse
A computer mouse is composed of several important parts that work together to make it function properly. By understanding these parts, we can better comprehend how a mouse works and how it allows us to interact with a computer.
A. Main Components Overview
Buttons:
A mouse usually has two buttons called the left button and the right button. These buttons are located on the top of the mouse, within easy reach of our fingers. The left button is used primarily for selecting and executing commands.
While the right button provides additional options or functions specific to the context.
Wheel:
The wheel is situated between the left and right buttons. It acts as a scrolling mechanism, enabling us to scroll up or down through documents, web pages, or other content on the screen.
By rolling the wheel, we can conveniently navigate through long texts or within a document or webpage.
Cable/Connector:
In the case of wired mouse, a cable extends from the mouse and connects to the computer’s USB port or other suitable ports. This cable ensures a stable and reliable connection between the mouse and the computer.
Which allowing them to communicate seamlessly.
Ball or Optical Sensors:
Older mechanical mouse use a small rubber or plastic ball that comes into contact with the surface beneath the mouse. As we move the mouse, the ball rotates and interacts with internal sensors, translating the movement into cursor motion on the screen.
However, modern optical or laser mouse use sensors like LEDs or lasers to track mouse movement without the need for a physical ball.
These sensors capture surface details and provide precise cursor movements.
LED or Laser:
Optical or laser mouse use light-emitting diodes (LEDs) or laser technology to illuminate the surface beneath the mouse.
The light emitted is reflected back into sensors, allowing the mouse to accurately detect its movement. This information is then sent to the computer, resulting in corresponding cursor movement on the screen.
Mouse Motherboard:
The mouse motherboard contains electronic components responsible for processing signals. And enabling communication between the mouse and the computer. Acting as a central hub, it allows the mouse to transmit input data and receive instructions from the computer.
B. Detailed Functions and Features of Each Part
Mouse Buttons:
The left button is primarily used for selecting, clicking, and executing commands. It is the most frequently used button on the mouse.
The right button provides additional functionality.
Such as accessing context menus or performing secondary actions.
Some computer mouse may have extra buttons that can be customized for specific tasks or preferences.
Mouse Wheel:
The wheel allows us to scroll vertically through documents, websites, or other content. By rolling the wheel up or down, we can easily navigate through lengthy texts or scrollable content.
Mouse Cable/Connector:
The cable connects the mouse to the computer’s USB port or other appropriate ports. It ensures a stable and reliable connection, enabling data transmission between the mouse and the computer.
Mouse Ball or Optical Sensors:
Mechanical mouse use a ball to detect movement, while optical or laser mouse use sensors to track mouse movement without a physical ball.
These sensors capture surface details, enabling precise cursor movements.
Mouse LED or Laser:
Optical or laser mouse use LEDs or lasers to illuminate the surface beneath the mouse, allowing accurate tracking of its movement.
This information is then translated into cursor movement on the screen.
Mouse Motherboard:
The mouse motherboard processes signals from the buttons, wheel, sensors, and other components. It facilitates communication between the mouse and the computer. Which ensuring smooth interaction and precise cursor control.
Understanding the different parts of a computer mouse is important. It helps us understand how the mouse works and how each component plays a role in its performance.
This knowledge allows us to make better choices when choosing a mouse and enables us to use its features more effectively.
Understanding the different parts of a computer mouse helps us maximize its functionality. Knowing the mouse components enhances our user experience.
So, let’s explore the parts of a computer mouse and discover how they contribute to its functionality.
Functions and Uses of a Computer Mouse
A computer mouse serves various functions and offers numerous uses that enhance our interaction with a computer.
Understanding these functions and uses allows us to harness the full potential of a mouse and improve our computing experience.
Pointing:
The mouse allows us to control the cursor on the screen, making it easier to select icons, navigate menus, and interact with graphical elements.
Selecting:
By clicking the left button, we can choose and manipulate text, files, or folders, simplifying our work with digital content.
Scrolling:
The mouse wheel enables us to navigate lengthy documents, web pages, or other scrollable content, making information access more efficient.
Drag and Drop:
With the mouse, we can move files, folders, and icons by clicking, holding, and relocating them on the screen.
Context Menu:
Right-clicking with the mouse brings up a menu with additional options and actions specific to the selected item or application.
Hovering:
When we hover the mouse pointer over an object, it can trigger interactive effects or display extra information, providing quick insights.
Gaming:
The mouse plays a crucial role in computer gaming, allowing precise control for actions like aiming, shooting, and navigating game environments.
Drawing and Graphics:
In graphic design or drawing applications, the mouse serves as a versatile tool for creating digital art and controlling brush strokes.
Accessibility:
For individuals with physical disabilities or limitations, the mouse offers an alternative input method, enabling them to navigate and perform tasks more easily.
Understanding and utilizing the functions of a computer mouse enhances productivity, efficiency, and enjoyment. Exploring its capabilities empowers us to navigate digital environments, interact with content, and perform tasks with ease.
Types of Computer Mouses!
Computer mouse come in various types, each designed to cater to different needs and preferences. Understanding the different types of computer mouse allows us to choose the one that best suits our requirements. And enhances our overall computing experience.
Wired Mouse:
The wired mouse connects to the computer using a cable that plugs into a USB port attached with motherboard. It provides a reliable and stable connection, ensuring seamless communication between the mouse and the computer.
Wireless Mouse:
Unlike the wired mouse, the wireless mouse uses wireless technology, such as Bluetooth or RF (radio frequency), to establish a connection with the computer. It offers freedom of movement and eliminates cable clutter on the desk.
Optical Mouse:
An optical mouse utilizes optical sensors to track movement. It uses LED (light-emitting diode) or laser technology to illuminate the surface beneath the mouse and detect changes in position, providing precise cursor control.
Laser Mouse:
Similar to an optical mouse, a laser mouse also employs laser technology for accurate tracking. It offers higher sensitivity and works on a wider range of surfaces compared to an optical mouse.
Gaming Mouse:
These are Designed specifically for gamers. Gaming mouse are equipped with additional features and customizable buttons. They offer higher sensitivity, adjustable DPI (dots per inch) settings, ergonomic designs. And programmable buttons for enhanced gaming performance.
Trackball Mouse:
A trackball mouse has a stationary ball on top that is manipulated by the user’s thumb or fingers. By rolling the ball, the cursor on the screen can be controlled, eliminating the need to move the entire mouse.
Touchpad:
Commonly found on laptops, touchpads are integrated into the laptop’s palm rest area. They allow users to control the cursor by gliding their fingers across the touch-sensitive surface.
Ergonomic Mouse:
Ergonomic mouse are designed with comfort and reduced strain in mind. They feature contoured shapes, special grips, and adjustable angles to provide a more natural and comfortable hand position during prolonged computer use.
By understanding the different types of computer mouse, we can choose the one that best suits our needs and preferences.
Choosing the right type of computer mouse is important for a comfortable and satisfying experience. There are different types to consider: wired or wireless, optical or laser, gaming, trackball, touchpad, and ergonomic.
Each type has its own advantages and features. Which can enhance our comfort, precision, and overall satisfaction when using the computer.
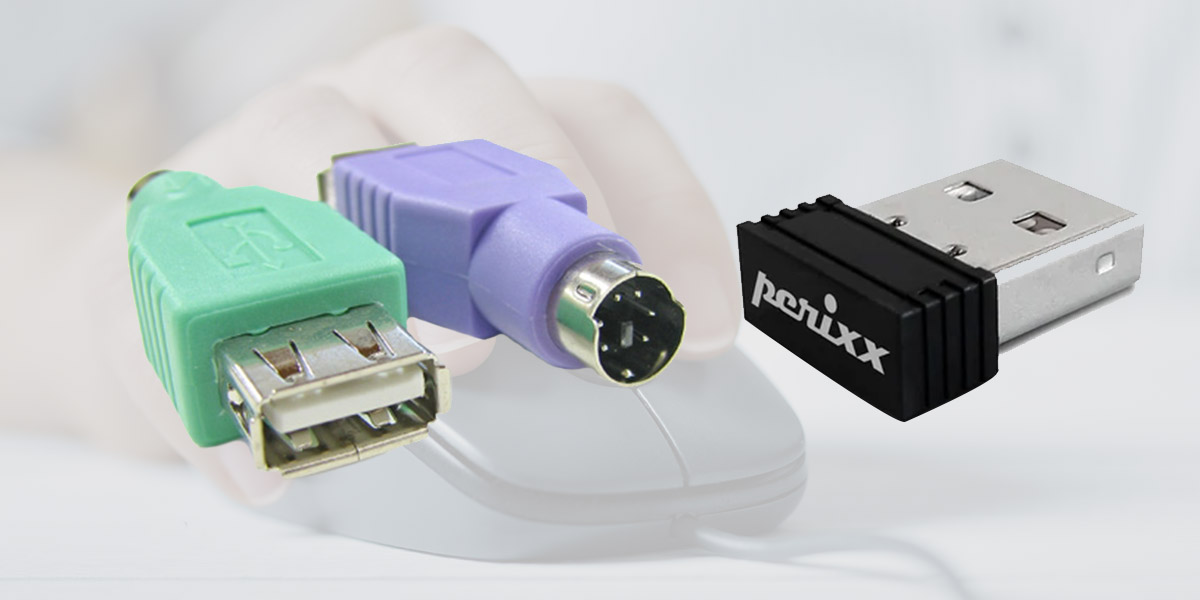
Computer Mouse Ports
Computer mouse connect to the computer using different types of ports. Understanding these ports enables us to properly connect and use our mouse with the computer.
USB Port:
The USB (Universal Serial Bus) port is the most common type of port used to connect computer mouse. It provides a fast and reliable connection, and most modern mouse are designed to connect to a USB port.
Simply plug the mouse’s USB cable into an available USB port on the computer, and it will be ready to use.
Bluetooth:
Some mouse utilize Bluetooth technology to establish a wireless connection with the computer. These mouse do not require a physical cable and instead communicate with the computer wirelessly.
To connect a Bluetooth mouse, ensure that your computer has Bluetooth capabilities and follow the pairing instructions provided with the mouse.
PS/2 Port:
Older computers may have a PS/2 port, which was commonly used for connecting keyboards and mouse.
The PS/2 port is a small round port, usually color-coded purple or green. If your computer has a PS/2 port, you can connect a PS/2 mouse to it using the appropriate connector.
Wireless Receiver:
For wireless mouse, a wireless receiver is used to establish the connection between the mouse and the computer.
The receiver is typically a small USB device that plugs into a USB port. It receives the wireless signal from the mouse and allows communication between the two.
Understanding the different ports and connectors used for computer mouse ensures that we can properly connect and use our mouse with the computer.
Whether it’s a USB port, Bluetooth, PS/2, or a wireless receiver, knowing the appropriate method for connecting our mouse ensures a smooth and seamless interaction with the computer.
Changing Mouse Properties!
Changing mouse properties allows us to customize its behavior and settings to suit our preferences.
By adjusting these settings, we can enhance our mouse experience and make it more comfortable and efficient to use.
Changing Button Configuration:
We can change the primary button configuration of the mouse, swapping the functions of the left and right buttons.
This is useful for left-handed individuals or those who prefer a different button setup.
Adjusting Double-Click Speed:
The double-click speed determines how quickly we need to press the mouse button twice for it to register as a double-click.
We can adjust this speed to match our clicking speed and make it easier to open files or select items.
Modifying Pointer Speed:
The pointer speed controls how fast the mouse cursor moves on the screen in response to our movements.
We can increase or decrease the pointer speed to achieve the desired cursor movement speed.
Enabling Pointer Trails:
Enabling pointer trails adds a trail or shadow behind the mouse cursor, making it easier to locate on the screen, especially for those with visual impairments.
The length and appearance of the trail can be customized.
Customizing Scroll Wheel Behavior:
We can customize how the scroll wheel behaves when scrolling through documents or web pages.
Options include scrolling multiple lines at a time or scrolling one page at a time.
Changing Mouse Sensitivity:
Mouse sensitivity determines the responsiveness of the mouse to our movements.
We can adjust the sensitivity to make the cursor move faster or slower based on our preferences.
Enhancing Accessibility Features:
Operating systems often provide accessibility features for individuals with disabilities. These features include options to adjust cursor size, color, and visibility.
Which caters to specific accessibility needs.
To change mouse properties, we can access the settings through the Control Panel. Or Settings menu of our computer’s operating system. Each operating system may have slightly different steps, but the options for customizing mouse properties are generally available.
By modifying mouse properties, we can tailor the mouse’s behavior to our liking and improve our overall user experience. Customizing button configuration, double-click speed, pointer speed, and other settings allows us to work more comfortably and efficiently, making the most out of our mouse.
Maintaining and Troubleshooting a Mouse
Taking care of our mouse and troubleshooting common issues can ensure its optimal performance. We can keep our mouse in good working condition by following these tips.
Cleaning:
Regularly cleaning the mouse can prevent dirt, dust, and debris from affecting its functionality. Use a soft cloth or cotton swab dipped in isopropyl alcohol to gently clean the exterior surfaces, buttons, and scroll wheel.
Avoid using excessive moisture or harsh cleaning agents.
Mouse Pad:
Using a mouse pad can provide a smooth and consistent surface for the mouse to glide on. It reduces friction and enhances tracking accuracy.
Choose a mouse pad suitable for your mouse type and ensure it is clean and free from dust or debris.
Adjusting Mouse Settings:
Customizing mouse settings according to personal preferences can improve comfort and control.
Access the mouse settings in the computer’s control panel or settings menu to adjust cursor speed, button functions, scroll wheel behavior, and other options.
Updating Drivers:
Keeping mouse drivers up to date ensures compatibility and may resolve compatibility issues or performance problems.
Visit the manufacturer’s website or use the computer’s device manager to check for driver updates.
Changing Batteries (Wireless Mouse):
If using a wireless mouse, monitor the battery level and replace them when needed. Low battery power can cause erratic cursor movement or connection issues.
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for battery replacement.
Troubleshooting Connectivity:
If the mouse is not working or experiencing connectivity issues, first check the connection between the mouse and the computer. For wired mouse, ensure the cable is securely connected to the USB port.
For wireless mouse, verify that the receiver is properly connected and within range.
Restarting the Computer:
Sometimes, restarting the computer can resolve temporary software or driver conflicts that may affect mouse functionality.
Try restarting the computer if the mouse is unresponsive or behaving unexpectedly.
Seeking Technical Support:
If troubleshooting steps do not resolve the issue, consult the manufacturer’s documentation or visit their support website for further assistance.
They may provide specific troubleshooting guides or offer customer support services.
By maintaining and troubleshooting our mouse, we can ensure its good condition and address issues promptly. This leads to a smooth and reliable mouse experience, allowing us to work efficiently without interruptions.
Mouse and Touchpad Alternatives
While the computer mouse is widely used, there are alternative input options available. These options cater to different preferences and needs. Exploring these alternatives helps us find the method that suits us best.
Touchpads:
Found on laptops, touchpads provide a built-in alternative to the mouse. By sensing touch and finger movements, we can control the cursor. And perform actions by tapping or swiping on the touch-sensitive surface.
Trackballs:
Trackballs offer a different way to control the cursor. Instead of moving the entire mouse, we use a stationary ball with our fingers. Trackballs are useful for precise control or limited desk space.
Stylus or Pen Input:
Some computers and tablets have touchscreens that support stylus or pen input. These devices allow precise control and are favored by artists, designers. And note-takers who prefer writing or drawing on the screen.
Voice Control:
Recent voice recognition advancements allow us to control computers with voice commands. It provides a hands-free input option. This benefits people with mobility impairments and those who prefer voice-based interaction.
Gesture Control:
Gesture control systems use cameras or sensors to detect hand movements and interpret them as commands. We can wave, swipe, or make specific gestures to control actions or navigate interfaces.
By exploring these alternatives, we can find the input method that suits our preferences, comfort, and specific needs.
Each alternative offers unique benefits that enhance our overall computing experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Computer Mouse:
Can I use a wireless mouse with any computer?
Yes, wireless mice generally use universal connectivity options such as USB or Bluetooth, allowing them to be used with most computers.
How do I clean my mouse?
To clean a mouse, gently wipe the surface with a soft cloth or a cotton swab dampened with a mild cleaning solution. Avoid using excessive moisture or harsh chemicals.
What should I do if my mouse cursor is not moving?
If your mouse cursor is not moving, try checking the cable connection (if using a wired mouse) or replacing the batteries (if using a wireless mouse). You can also try restarting your computer or updating the mouse drivers.
Can I customize the mouse buttons?
Many mice come with software that allows you to customize the buttons and assign specific functions or macros. Check the manufacturer’s website for any available software or drivers for your mouse model.
Are there ergonomic options available for people with hand or wrist discomfort?
Yes, there are ergonomic mouse available that are designed to provide more comfort and reduce strain on the hand and wrist. These mice often feature an ergonomic shape, adjustable angles, and special grips.
Can I use a mouse with a laptop touchpad?
Yes, you can use a mouse with a laptop. Simply plug in a wired mouse to a USB port or connect a wireless mouse via Bluetooth or a USB receiver. Most laptops also have settings that allow you to disable the touchpad while using an external mouse.
How can I change the mouse settings on my computer?
On Windows OS, you can change mouse settings by going to the Control Panel or the Settings menu and selecting the “Mouse” or “Mouse and Touchpad” options. On Mac, you can access mouse settings in the System Preferences menu under “Mouse” or “Trackpad.”