What Is a Power Supply and How Does It Work?
Today I am going to share my finding and understanding about a most important component of a computer which you may interact sometime; somehow. It is known as the power supply, which is one of the most crucial components of a computer and you should get some knowledge about it’s important to understand how they works.
When we operate a computer; we all use power supplies every day, and many don’t realize that a power supply is a transformer.
The fact is; all devices that require electricity are powered by a power supply, even the battery-powered ones.
If you are curious to know more about it, when you check inside your computer body, you’ll find a power supply that converts the alternating current (AC) coming from the wall outlet into the direct current (DC) to run your PC.
A power supply is a device that provides electrical energy to one or more electric loads.
The term is most commonly used to refer to an AC/DC adapter that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC), as required by most electronic devices.
Let’s discuss little deep about this topic to understand more:-
What is a Power Supply in simple words?
“An electrical load is supplied with electric power by a power supply. An electric power supply converts one form of electrical energy into another, hence the name electric power converter.”
A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to an electrical device or system.
The term is most commonly used to refer to devices that convert one form of electrical energy into another, such as AC/DC power adapters and batteries.
Power supplies may also include devices that regulate the voltage or current supplied to an electrical device or system.
What are three purposes of a power supply?
A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to an electrical load.
The three main purposes of a power supply are to convert one form of electrical energy into another, to store energy, and to regulate the voltage and current supplied to the load.
1. Conversion of energy: Power supplies are used to convert one form of electrical energy into another. The most common type of power supply is the alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) converter. AC to DC converters are used in a wide variety of electronic devices, from computers and office equipment to industrial machinery.
2. Storage of energy: Many power supplies are designed to store energy so that it can be released into the electrical load when needed.
This type of power supply is called a battery. Batteries are commonly used in portable electronic devices, such as laptops and cell phones, where there is no access to an AC power source.
3. Regulation of voltage and current: Power supplies are also used to regulate the voltage and current supplied to the electrical load.
Voltage regulators are used in electronic devices that require a constant voltage, such as computers and audio equipment.
Current regulators are used in electronic devices that require a constant current.
Power supplies are essential components of electronic devices.
They provide the power necessary to run the device and perform its functions.
Without a power supply, electronic devices would not be able to operate.
Power Supply Linear & Switched Mode:
These can be categorized into two general types: linear and switched mode. Transformers used in linear power supplies convert the input voltage into a different, generally higher voltage.
1. Linear Power supplies: The transformer steps up the voltage while stepping down the current, so linear power supplies are typically large and heavy. In addition, linear power supplies are less efficient than switched-mode power supplies and generate more heat.
However, linear power supplies tend to be more stable and have better regulation than switched-mode power supplies.
2. Switched-mode power supplies use electronic components to convert the input voltage into a high-frequency alternating current (AC).
This AC is then converted back into DC by another electronic component called a rectifier. Switched-mode power supplies are mu1ch lighter and smaller than linear power supplies because they don’t require a large transformer.
In addition, they’re much more efficient since they don’t waste as much energy in the form of heat. However, switched-mode power supplies can generate
What Does a Power Supply Do?
A power supply is a device that provides power to an electrical system. It can be either a standalone unit or part of a larger system.
A power supply has a number of important functions, including providing the correct amount of power to the system, protecting the system from damage, and regulating the voltage level.
There is a possibility that the power supply is internal or external to the device. An electric power supply’s function is to convert electric power between different forms and to deliver it to the load.
5 function of Power Supply:
- To provide power to the components of a system
- To regulate and control the voltage and current supplied to the system
- To protect the components from damage due to overvoltage, undervoltage, or overload
- To convert the AC input voltage to the DC output voltage required by the system
- To To provide provide isolation isolation between between the the input input and and output output volt voltagesages
Internal power supplies are found in devices such as computers and servers. External power supplies are used with devices such as portable computers, office equipment, and appliances.
What are the 3 types of Power Supply?
There are three main types of power supplies:
- AC (alternating current),
- DC (direct current),
- and batteries.
AC power supplies are the most common type, as they are used in homes and businesses to provide electricity.
DC power supplies are used in devices that require a constant flow of electric current, such as computers and TVs.
Batteries are used in portable devices that need to be able to operate without being plugged into an outlet.
Power supplies are classified according to their output voltage and current. The output voltage is the voltage that is delivered to the load. The output current is the current that is delivered to the load.
They are rated in terms of watts, which is a measure of the amount of work they can do over time. As the wattage increases, the power supply becomes more powerful.
Power supplies can also be efficiency rated, which measures how well they convert energy from one form to another. A higher efficiency rating means less wasted energy and lower operating costs.
How Does a Power Supply Work in Computer? Power Supply Diagram!
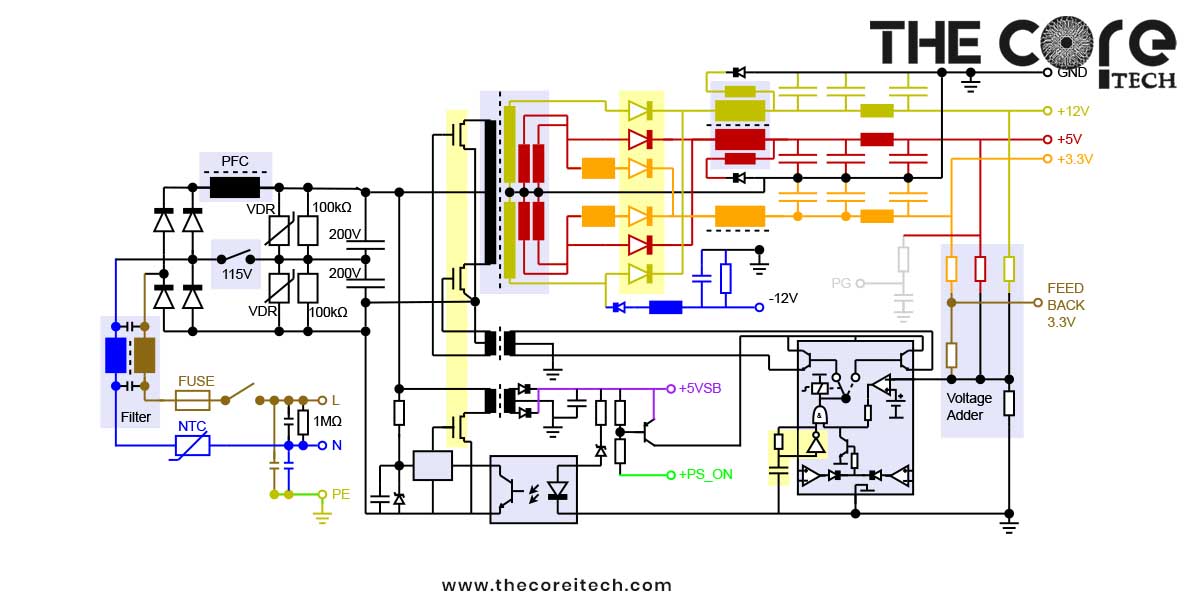
The power supply provides electricity to another electronic device. It converts one form of energy into another form, usually electric potential energy. The most common type of power supply is a battery. Other types include fuel cells, solar cells, generators, and transformers.
A power supply converts one form of energy into another form. The most common type of power supply in computer is a battery. Other types include fuel cells, solar cells, generators, and transformers.
The basic principle behind all power supplies is conversion. In order to convert one form of energy into another, the power supply must first store the energy in some way.
This can be done using capacitors, inductors, or batteries. Once the energy is stored, the power supply uses special circuits to convert it into the desired form.
Capacitors store energy in an electric field, while inductors store it in a magnetic field. Likewise, batteries can be converted into electrical power through chemical energy.
Parts of a Power Supply and Their Functions
A power supply is made up of a few various parts, each with its own function. The most important part of a power supply is the transformer.
- Transformer
The transformer steps up or steps down the voltage from the AC line to the DC voltage that is used by the computer.
- Rectifier
The rectifier diodes convert the AC voltage from the transformer to DC voltage. The capacitor filters out any AC ripple that may be present in the DC voltage.
- Regulator
Finally, the regulator regulates the DC voltage to a level that is safe for the components in the computer.
How Does a Power Supply Convert AC to DC?
In homes and businesses, alternating current (AC) is frequently used.
But many electronic devices require direct current (DC).
So, how does a power supply take AC and convert it into DC?
- Rectification
Power supplies use a process called rectification to convert AC into DC. The term “rectification” simply means converting the alternating current into direct current.
It’s done by using a device called a rectifier, which contains one or more diodes.
Electronic devices, diodes are semiconductor devices that allow electricity to flow only in one direction.
- Bridge Circuit
The rectifier contains two sets of diodes arranged in what’s called a bridge circuit. The diodes are connected to the AC source on one side and to the load on the other side.
When the AC source is first connected to the rectifier, the diodes are not conducting because they don’t have enough voltage across them.
This causes a brief surge of current, which is absorbed by a capacitor.
Once the capacitor has been charged, the diode bridge starts conducting and electric current flows through the load.
The load can be anything from a simple light bulb to a complex electronic device.
The current flowing through the load will be pulsating DC because
How to use dc Power Supply?
In order to use a DC power supply, you will need to connect the positive lead of the power supply to the positive terminal of your load, and the negative lead of the power supply to the negative terminal of your load.
Depending on the specific type of DC power supply you are using, you may also need to connect a ground lead to the ground terminal of your load.
If you are using a regulated DC power supply, you will need to set the voltage output of the power supply to the desired level before connecting it to your load. To do this, you will use the voltage control knob on the front of the power supply.
Once you have set the voltage output, you can then connect the power supply to your load.
If you are using an unregulated DC power supply, you will not need to set the voltage output before connecting it to your load.
However, you should always check the voltage output of the power supply with a voltmeter before connecting it to your load, to make sure that it is set to the correct level.
Once you have connected the DC power supply to your load, you can then turn on the power switch to begin supplying power to your load.
Who Needs Power Supply?
In my personal experience; we all know that feeling, while you are working hard and making great progress, your computer suddenly shuts down.
No warning, no redeeming quality, it just shuts down, taking all your challenging work with it.
For laptops and other portable devices, power supplies are an essential part of keeping them running.
But what about desktop computers?
Do they need power supplies?
The short answer is yes, every computer needs a power supply. But there is a little more to it than that.
Let’s take a closer look at power supplies and why every computer needs one.
In order to power the components inside a computer, alternating current (AC) from the outlet must be converted into direct current (DC). Depending on their wattage capacity, power supplies can deliver different amounts of power.
For desktop computers, the power supply should be strong enough to handle all the components. It is possible for the motherboard, processor, graphics card, hard disk, and other components to require their own dedicated power supply. If the power supply isn’t strong enough, it could cause problems with stability or even damage the components.
So, in short, every person who owns a computer or deals with any electronic device needs a power supply. To name some see the following list:
- Designers
- Engineers
- Military officers
- Doctors
- Freelancers
- Teachers etc.
Conclusion of Power Supply Guide!
Electricity is provided by a power supply to a load in electrical engineering. Often referred to as power converters, power supplies are designed to convert one form of electrical energy into another.
They are also occasionally called power conditioners, though this term is more often used to refer to devices that regulate the quality of the power rather than its quantity.
Almost all power supplies convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). These types of power supplies are known as AC-to-DC converters or rectifiers. Other common power supplies include DC-to-DC converters and DC-to-AC inverters.
Power supplies are used in a wide variety of electronic devices, including computers, cell phone chargers, and televisions. Many electronic devices require multiple voltages, and as a result, most power supplies contain more than one output.








