Inside the World of Graphics Cards: A complete guide How GPU works?
Get ready to delve into the captivating world of graphics cards and discover how they play a vital role in driving visual computing.
In this guide, I’ll explore the fascinating technology behind stunning visuals in games, movies, and various other applications. Gain a deeper understanding of the inner workings of graphics cards and their impact on delivering immersive visual experiences.
I’ll discuss the key components like the GPU and VRAM.
The GPU is the brain of the graphics card, executing calculations for rendering. VRAM stores and processes data for quick access, ensuring smooth performance.
Cooling systems in graphics cards regulate GPU temperature. They include fans and heat sinks to prevent overheating and maintain optimal performance.
Connectors and ports on graphics cards allow easy connections to display devices like monitors and TVs.
I’ll explore the graphics pipeline, the step-by-step process of rendering. Techniques like rasterization and ray tracing impact visual quality.
GPU architecture determines a graphics card’s capabilities and performance. NVIDIA CUDA and AMD RDNA are examples of architectures. Which use parallel processing and shader units.
Graphics drivers and software ease communication between the operating system and graphics hardware. Keeping drivers updated is important for compatibility and performance.
I’ll glimpse into the future of graphics cards. Exploring technologies like real-time ray tracing and DLSS. Integration of graphics cards into mobile devices and VR headsets offers exciting possibilities.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid understanding of graphics cards. Also their impact on visual computing. Let’s dive into the captivating world of graphics cards!
Components of a Graphics card!
A graphics card comprises essential components that work together to deliver impressive visuals:
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)
The GPU is the powerhouse behind the graphics card. It performs complex calculations for rendering images, videos, and animations.
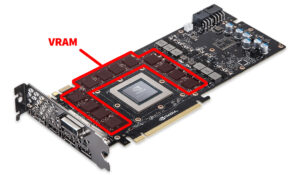
VRAM (Video Random Access Memory)
VRAM is dedicated memory that stores and processes graphics data for quick access. Enough VRAM capacity ensures smooth performance and handles demanding visual tasks.
Cooling System
Graphics cards have cooling systems with fans and heat sinks to prevent overheating. Effective cooling maintains optimal performance and extends the card’s lifespan.
Connectors and Ports
Graphics cards feature connectors and ports for seamless connections to displays. These connectors, such as HDMI, ensure effortless integration with a wide range of display devices. These enable high-quality visual output.
Understanding these components is essential to comprehend how graphics cards function. It forms the foundation for appreciating their role in enhancing the visual computing experience.
Cooling system!
Graphics cards have a cooling system to prevent overheating and maintain performance. Here’s how it works:
Fans
Graphics cards use fans to circulate air, keeping the GPU and other components cool. Fans draw in cool air and expel hot air, ensuring proper ventilation.
Heat sinks
Heat sinks, with their fins, absorb and dissipate heat from the GPU. They increase the surface area for efficient heat transfer.
Thermal paste
Thermal paste is applied between the GPU and heat sink. It enhances heat conductivity by filling microscopic gaps, ensuring effective thermal transfer.
Heat pipes (in some cooling systems)
Heat pipes, filled with a special fluid, connect the GPU to the heat sink. They transfer heat efficiently, using evaporation and condensation.
Additional mechanisms (in high-end cards)
Advanced cooling systems may include vapor chambers or liquid cooling for improved heat dissipation and temperature control.
By employing these cooling techniques, graphics cards maintain optimal performance and prevent overheating. Ensuring smooth operation even during demanding tasks. Effective cooling is crucial to prevent thermal throttling and protect the longevity of the graphics card components.
Connectors and ports:
Graphics cards come equipped with various connectors and ports. Which enable seamless connections to different display devices such as monitors and TVs.
Let’s explore the details in steps:
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface):
HDMI is a widely used connector found on graphics cards. It allows the transmission of high-definition audio and video signals through a single cable.
Simply connect one end of an HDMI cable to the graphics card’s HDMI port. And the other end to the corresponding HDMI port on your display device.
DisplayPort:
DisplayPort is another popular connector commonly found on graphics cards. It supports high-resolution displays and provides enhanced flexibility for multi-monitor setups.
Similar to HDMI, you can connect a DisplayPort cable. Directory from the graphics card’s DisplayPort output to the DisplayPort input.
DVI (Digital Visual Interface):
DVI is a digital connector that supports both digital and analog signals. Graphics cards often feature DVI ports, allowing you to connect to older display devices.
Which do not have HDMI or DisplayPort inputs.
Depending on the graphics card, you may find DVI-I (integrated), DVI-D (digital-only), or DVI-A (analog-only) ports.
VGA (Video Graphics Array):
While becoming less common, some graphics cards still include VGA ports. VGA is an analog connector primarily used for older monitors.
If your display device only has a VGA input, you can connect it to the VGA port on the graphics card.
You can use a VGA cable or by using a VGA-to-DVI or VGA-to-HDMI adapter.
Other ports:
Graphics cards may also feature additional ports. Such as DisplayPort++, mini DisplayPort, or USB-C with DisplayPort Alt Mode.
These ports offer compatibility with a variety of display devices. And adapters, expanding connectivity options.
By having a range of connectors and ports, graphics cards ensure compatibility with different display devices, allowing you to enjoy high-quality visuals.
Choose the appropriate connector based on your display device’s available inputs and the graphics card’s supported outputs to establish a seamless connection and experience immersive visuals.
Graphics Drivers and Software!
Graphics drivers and software are crucial for smooth communication between the OS and graphics hardware. They play a crucial role in ensuring seamless functionality.
Let’s examine the details in steps:
Operating System compatibility
Graphics drivers are designed to be compatible with specific operating systems such as
- Windows
- macOS
- or Linux.
When installing a graphics card, make sure to download the correct driver version for your OS. This ensures proper functionality and optimal performance.
Communication interface
Graphics drivers serve as an intermediary between the OS and the graphics hardware. They ease the exchange of information and commands.
Which allowing the OS to control and utilize the capabilities of the GC .
Hardware optimization
Graphics drivers include optimizations tailored for specific graphics cards. These optimizations aim to maximize performance, improve stability.
Also enhance compatibility with various applications and games. updating the graphics driver is essential.
Which ensures that you can enjoy from the latest optimizations and bug fixes.
Graphics settings and control panel
Graphics drivers often come bundled with control panel software. These provides access to various settings and customization options. You can adjust display properties, configure many monitors, enable features.
Like anti-aliasing or vertical synchronization, and fine-tune graphics performance to suit your preferences.
Updates and compatibility
Graphics driver updates are released by the graphics card manufacturer.
These updates address software bugs, improve compatibility with new applications. It also may introduce performance optimizations. Keeping your graphics driver up to date is essential.
For maintaining system stability, improving compatibility, and ensuring optimal performance.
Additional software and features
Some graphics drivers offer extra software or features. For example, NVIDIA’s GeForce Experience provides automatic driver updates.
Also game optimizations, and gameplay recording/streaming features. AMD’s Radeon Software offers similar features, including performance tuning and streaming capabilities.
These software packages enhance the user experience and provide added functionality.
Graphics drivers and software are vital for seamless GC operation. Keep them up-to-date to optimize performance and customize settings. Ensure compatibility with the latest applications and games to enhance your VC experience.
Future trends and advancements
The world of graphics cards is constantly evolving, with new technologies and advancements on the horizon. Here are some key future trends to keep an eye on:
Ray tracing:
Ray tracing is a rendering technique that simulates the behavior of light in a scene. Resulting in highly realistic and immersive visuals.
As graphics cards become more powerful, ray tracing capabilities are expected to be further enhanced.
Also enabling even more realistic lighting and reflections in games and other applications.
AI-powered graphics:
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly being utilized in graphics processing. AI-powered techniques, such as machine learning-based upscaling and image enhancement. It can also improve graphics quality and performance.
As AI continues to advance, we can expect more sophisticated AI algorithms to be integrated into graphics cards. Which also can be delivering stunning visuals in real-time.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR):
VR and AR technologies are rapidly growing in popularity. Graphics cards will play a crucial role in driving the immersive experiences of these technologies.
Future advancements may include higher resolutions, increased refresh rates, and improved tracking capabilities.
Which may allow even more realistic and engaging VR and AR experiences.
Power efficiency:
Graphics card manufacturers are increasingly focusing on power efficiency.
Future graphics cards will boast higher performance and lower power consumption.
Thanks to advancements in manufacturing and architecture. This reduces energy usage, minimizes heat output, and improves system stability.
Multi-GPU configurations:
Multi-GPU setups are common in gaming, but future advancements may streamline and simplify them.
This could lead to improved performance and support for higher resolutions.
And demanding workloads, making multi-GPU configurations more accessible and user-friendly.
Graphics cards’ future trends shape visual computing, enabling immersive experiences. Witness the transformation of digital content interaction through these developments.
Integration of graphics cards in other devices
Graphics cards are integrated into diverse devices beyond desktop computers. Here’s a detailed look:
Laptops and Notebooks:
These devices incorporate dedicated graphics cards for improved graphical capabilities in gaming, video editing, and graphic design.
Gaming Consoles:
PlayStation, Xbox, and Nintendo Switch employ specialized GPUs for high-quality graphics and immersive gaming experiences.
Mobile Devices:
High-end smartphones and tablets feature integrated graphics chips to handle graphics-intensive tasks like mobile gaming and video playback.
All-in-One Computers:
AIO computers combine desktop components, including integrated graphics cards, into a single unit for everyday tasks and multimedia consumption.
Set-Top Boxes and Streaming Devices:
GPUs integrated into these devices ensure smooth streaming of HD video content by handling video decoding and rendering.
Virtual Reality (VR) Devices:
Powerful graphics cards are essential in VR headsets to render realistic virtual environments and provide smooth motion tracking.
The integration of graphics cards across these devices highlights their significance in delivering superior visual experiences in laptops, gaming consoles, mobile devices, AIO computers, set-top boxes, and VR devices.
Conclusion
Graphics cards play a vital role in driving visual computing across a range of devices. From desktop computers to laptops, gaming consoles, mobile devices, all-in-one computers, set-top boxes, and virtual reality devices, the integration of graphics cards enhances graphical capabilities and delivers immersive experiences. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in graphics cards, opening up new possibilities for realistic and visually captivating digital content.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a graphics card?
A graphics card, also known as a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), is a hardware component that handles the rendering and display of visual content on a computer or other devices. It is responsible for generating and processing images, videos, and 3D graphics.
Why do I need a graphics card?
A graphics card is essential for tasks that require intense graphical processing, such as gaming, video editing, 3D modeling, and running graphic-intensive applications. It offloads the processing from the computer’s CPU, resulting in smoother performance, enhanced visuals, and improved overall user experience.
How does a graphics card work?
A graphics card works by receiving data from the CPU and rendering it into images that can be displayed on a monitor or other output devices. It consists of a GPU, video memory (VRAM), and various components that process and transform data to create the final image that you see on your screen.
Can I upgrade my graphics card?
In most cases, graphics cards can be upgraded on desktop computers, allowing you to replace an older or lower-performing card with a newer, more powerful one. However, the upgradeability depends on the compatibility of the card with your system’s motherboard and power supply.
What is the difference between integrated and dedicated graphics?
Integrated graphics refer to graphics processing capabilities integrated into the computer’s CPU, while dedicated graphics cards are separate hardware components designed specifically for graphics processing. Dedicated graphics cards offer higher performance and are more suitable for demanding tasks like gaming and professional applications.
How do I install graphics card drivers?
To install graphics card drivers, you can typically download them from the manufacturer’s website or use the driver installation software provided. Once downloaded, run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions to install the drivers specific to your graphics card and operating system.
What is overclocking, and should I overclock my graphics card?
Overclocking is the process of increasing the clock speed and performance of a graphics card beyond its default settings to achieve higher performance. It can provide a performance boost but also generates more heat and may void the warranty. Overclocking should be done with caution and proper cooling measures in place.
Can I use multiple graphics cards in my system?
Yes, it is possible to use multiple graphics cards in some systems. This configuration, known as SLI (Scalable Link Interface) for Nvidia cards or CrossFire for AMD cards, allows two or more cards to work together to enhance graphics performance. However, not all applications or games support multi-GPU setups, and compatibility with your motherboard and power supply must be considered.
How often should I update my graphics card drivers?
It is recommended to update your graphics card drivers periodically, especially when experiencing issues, or when new games or applications require updated driver versions. Check the manufacturer’s website regularly for driver updates, or use automatic driver update software to ensure you have the latest drivers installed.
Are graphics cards only for gaming?
While graphics cards are commonly associated with gaming, they are also used for various other tasks. They are crucial for professional applications like video editing, 3D modeling, animation, and scientific simulations that require extensive graphical processing power.
Remember that specific details and recommendations may vary depending on your specific hardware and software configuration, so it’s always best to consult official documentation or seek support from the manufacturer for personalized assistance.